Where does glycolysis occur: Glycolysis is one of living organisms’ most important metabolic pathways, yet it is commonly misunderstood? This process plays a critical role in energy metabolism, but many people are unaware of glycolysis and where it occurs within our bodies.
In this article, we’ll dive into the details to explain exactly what glycolysis does and why it’s so important for our daily functioning. Whether you’re studying biochemistry or simply curious about how your body generates energy, understanding glycolysis will help you appreciate its significance as a fundamental building block of life!
What is Glycolysis?
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that takes place in the cytosol of cells and converts glucose into pyruvate, releasing energy in the form of ATP. It is the first stage of cellular respiration, which breaks down food molecules to produce energy for the cell.
Why Is Glycolysis Important For Body Functioning?
Glycolysis is a critical metabolic pathway for energy production in our bodies. It helps to break down glucose, a type of sugar found in food, and convert it into energy that can be used by the body’s cells. This energy is essential for many bodily functions and processes, such as muscle movement and digestion.
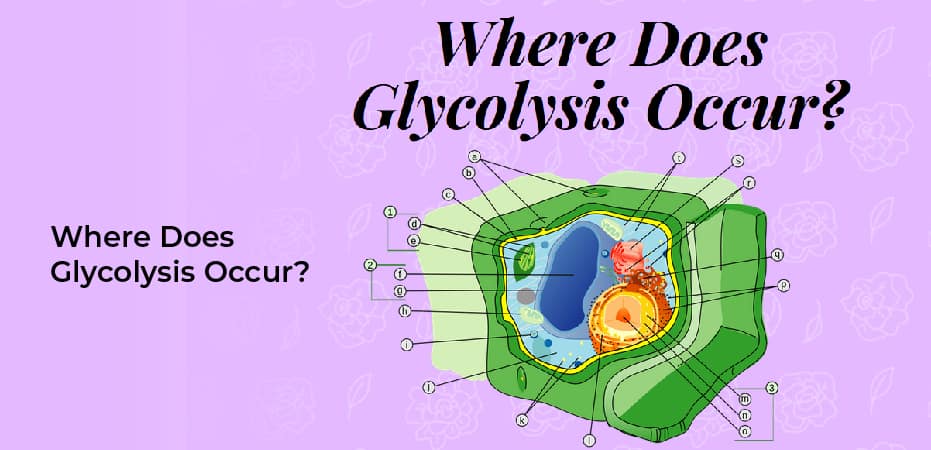
Where Does Glycolysis Occur In The Body?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol of cells throughout the body. It is a key energy-producing pathway that takes place in all forms of life, from bacteria to humans. In animals and plants, glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of their cells, while in single-celled organisms, it occurs in the cell membrane. Glycolysis is an important part of cellular respiration and is essential for energy production in all organisms.
In humans, glycolysis occurs in every type of tissue and plays a critical role in providing energy for many bodily functions. It is especially important for energy-demanding tissues such as muscle and brain tissue.
What Are The Benefits Of Glycolysis In Our Human Body?
Glycolysis is essential for energy production in our bodies. It helps to break down glucose, a type of sugar found in our food, and convert it into energy that can be used by the body’s cells. Glycolysis also produces molecules important for other metabolic processes, such as fatty and amino acids.
Moreover, glycolysis helps regulate blood sugar levels by ensuring that glucose is used quickly and efficiently. This human body glycolysis plays an important role in maintaining our body’s acid-base balance by producing acids that other processes can neutralize.
What Role Does Glycolysis Play In Energy Production For The Body Cells?
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration, which breaks down food molecules to produce energy for the cell. During glycolysis, glucose molecules are broken down into pyruvate molecules, releasing energy as ATP. This ATP is then used by cells to power metabolic processes and other activities. Glycolysis is an important process for energy production in all organisms, and it is especially important for energy-demanding tissues like muscle and brain tissue.
Diseases Caused By The Inability To Produce Sufficient Insulin
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects your body’s ability to use insulin effectively. When your body cannot make enough insulin, the glucose in your blood can’t be moved into your cells. This causes many complications. Some of these include obesity, high blood pressure, and kidney problems.
Insulin is a hormone that’s produced by your pancreas. It’s designed to help your body move glucose from the blood into your muscle, fat, and liver cells. However, as the years go by, your body becomes less sensitive to the hormone. Therefore, your pancreas produces less and less insulin. The result is that your blood sugar levels are elevated. These elevated blood sugar levels can cause a variety of symptoms.
In some cases, the immune system attacks the cells that produce insulin. This leads to an autoimmune disease called type 1 diabetes. Usually diagnosed in children and teens, type 1 diabetes requires daily insulin injections.
Type 2 diabetes is an illness that is caused by the inability of the body to produce adequate amounts of insulin. Usually diagnosed in middle age or older, type 2 diabetes is characterized by an abnormally high blood glucose level.