Osmosis is a fascinating process that happens all around us, yet many of us don’t understand it. Whether it’s the exchange of water molecules in our cells or saltwater seeping into land soil, osmosis affects our everyday lives and intricate ecosystems worldwide. But what exactly is osmosis, why does it happen, and when does it occur? In this blog post, we explore these questions and provide an overview of just how powerful an effect osmosis can have!
What is Osmosis& Its Types?
Osmosis is the process of moving water molecules from a high-concentration solution into a low-concentration solution through a semi-permeable membrane. In biology, it is used to regulate cell movement, nutrient absorption, and the internal environment of an organism.
Osmosis has several different forms, which are based on the type of membrane that the solute is dissolved in. here are the following below:
- Diffusion-Osmosis:
- Reverse Osmosis:Reverse osmosis is a process that is used to separate water from salts and other dissolved solids. The process takes the pressure and forces water through a semi-permeable membrane.
- Crystalloid Osmosisis the process of exchanging solutes between two solutions. It can be used in biotechnology to create highly concentrated solutions or to separate proteins and other molecules.
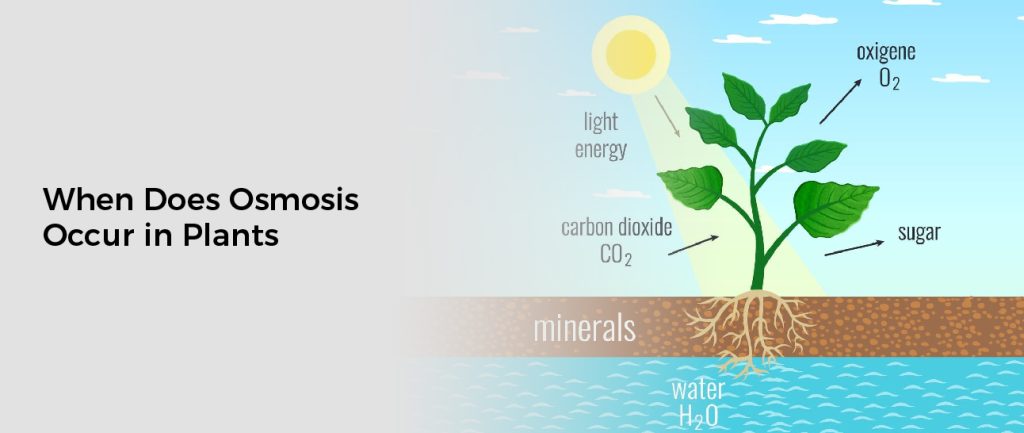
When Does Osmosis Occur in Plants
Osmosis occurs when a plant is placed in a solution of solutes, such as sugar or salt. When this happens, water moves through the cell membrane and into the cell’s vacuole, where it becomes concentrated. This process can be reversed if the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane is equalized. When this happens, water moves in the opposite direction, from the cell to the external solution. This is known as reverse osmosis.
How Does Osmosis Occur in Plant Ecological System
Osmosis occurs within a plant’s ecological system, as it constantly exchanges water and nutrients between its cells, the external environment, and other organisms. When a plant is placed in a solution with solutes of varying concentrations, osmosis occurs as water moves from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This process helps plants absorb water and nutrients while transporting them throughout their cellular structure.
Moreover, when a plant is exposed to extreme environmental conditions, such as drought or flooding, osmosis can also help it maintain homeostasis. When a plant is placed in an area with high concentrations of solutes, water is drawn out of the cell and into the external environment. This helps protect the plant from damage caused by excessive moisture or salt levels.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Osmosis in Plants
The rate of osmosis in plants is affected by a variety of factors, including:
- The type and concentration of solutes in the external environment.
- The size, shape, and permeability of the cell membrane.
- The temperature of the environment.
- The pH level of the surrounding solution.
- The presence of certain proteins or enzymes.
- The amount of water in the environment.
Applications Of Osmosis in Biotechnology and Medicine
Osmosis is used in biotechnology and medicine to separate materials, such as proteins, DNA, and enzymes. Osmotic pressure can be used to concentrate and purify solutions for medical or research purposes. It is also used in the production of certain drugs and medicines.
Osmosis also plays an important role in the transplantation of organs and tissues. When organs or tissues are transplanted from one person to another, osmosis ensures that the transplant is compatible with the new host’s body. This process helps balance the salt concentration in both the donor tissue and the recipient body so that the organ can be accepted without any risk of rejection.
In addition, osmosis is used in the food industry to preserve fruits and vegetables. When foods are placed in high-solute solutions, they become dehydrated and can be stored for longer periods. This process also helps reduce spoilage caused by microorganisms like fungi and bacteria.
Electron Diffusion Vs. Gaseous Diffusion
Osmosis is a chemical process involving water molecules’ movement through a permeable membrane. The movement takes place in a liquid state, but it can also take place in a gaseous state. Typically, the molecules are moved from a higher to a lower concentration, and only water is involved in this process.
While osmosis and diffusion are two distinct processes, they are related. The difference is the fact that osmosis takes place over a short distance. In contrast, diffusion takes place over a wide range of distances.
The osmosis phenomenon is often the result of the interaction between water and salt ions. As the salt concentration near the membrane surface increases, so does the membrane’s permeability. A more concentrated feed salt solution requires a higher hydraulic pressure and greater permeate water flux.
In order to understand the salt-water separation mechanisms of reverse osmosis membranes, it is important to recognize the various effects. These include diffusion, osmosis, and electromigration. Each effect has its specific molecular mechanism and requires treatment separately.