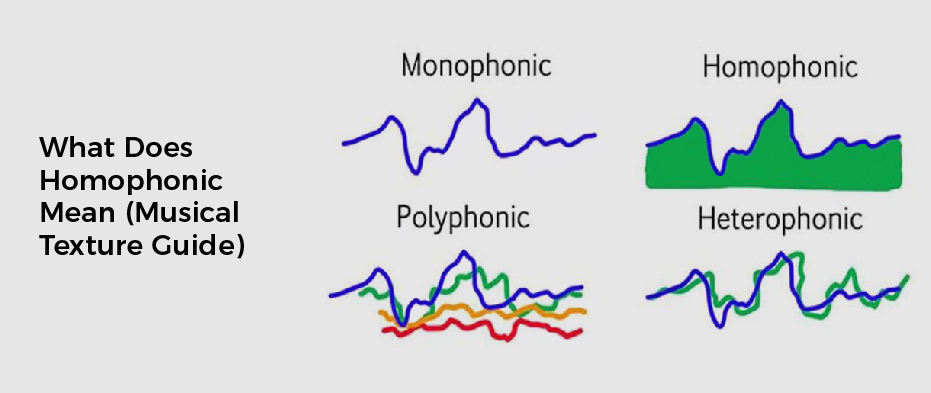
When it comes to music, you’ll want to understand what the term Homophonic means. This term is used to describe choral music. The definition of the term can vary, but it can also refer to other types of musical textures, such as polyphonic and heterophonic.
Homophonic music typically involves a single melody or voice, with the other voices providing harmonies and accompaniment. What’s great about this type of music is that it can be both simple and complex, depending on the composer. Whether you’re listening to classical pieces or pop songs, understanding what homophony is will give you a better appreciation for the music.
Each voice has its own unique rhythm and melody with homophonic music, but they all must agree on the same pitch to be considered homophony. However,each voice may feature a different texture or move in different directions, leading to an interesting sound that can capture any given music piece’s emotions.
About Homophonic
Homophonic is a type of musical texture that involves two or more voices singing or playing the same melody but with different rhythms, leading to an interesting and varied sound.This type of texture has been used in many styles of music, including pop, rock, jazz, and classical.
What makes homophony unique is that each voice has its own part and works together to add depth and interest to the overall sound. Homo-phonic music typically features the main melody, with accompanying harmony parts that follow a similar pattern or theme.
Each voice may have its unique rhythm, but all voices must agree on the same pitch for it to be considered homophony.
The Choral Musical Texture of Homophonic
The most common type of homo-phonic texture is choral. This type of texture involves a group of singers, such as a choir or chorus, singing in harmony with each other and usually following a leader’s melody line. The individual voices may be singing different words or syllables, but all must agree on the same note. This type of texture has been used in various types of music, including religious services, operas, and popular songs.
1. Heterophonic Texture
The homophonic heterophonic texture is a type of musical texture. It is characterized by a single melody played by one voice over a choral accompaniment. The melody is then supported by various parts, such as lower strings, which play a different rhythm.
The term is derived from the Greek words for “same-sounding” and “sound.” Generally, the melody and accompaniment move in the same rhythm, but not always. It is also possible for each part to be slightly different, such as in a piano-vocal duet.
The main difference between the homophonic heterophonic texture and polyphonic music is the presence of a single melody. This melody is often performed by several voices, creating a multi-voiced texture.Using this method, many contemporary songs are created. These include “Bliss” by Schubert, which features a piano melody while the singer sings the words.
2. Homorhythmic Texture
The homorhythmic texture is a type of music texture that is characterized by all parts of the melody or harmony being played in the same rhythm. It is often associated with choral music and may also be found in other styles of music, such as jazz and rock.
While this is a common music texture, it is not as commonly used as other types of textures, such as polyphony and monophony. It can be used to create chord changes but is not used for long periods.Using this texture, composers are able to create a wide range of effects. For example, one note may sound a little different than another, while a different instrument might provide a new rhythm to the song.
The homorhythmic texture is used in a number of styles, from the most classical to pop. For example, Bach’s inventions are a perfect example of weaving melodies together to create a whole.
3. Homophonic Choral Music
Homophonic choral music is a musical texture where instruments or other voices accompany a melody. The term is derived from the Greek word homophonia, meaning “similar.” There are two types of homo-phonic textures: polyphonic and heterophonic.
Both are used in Western music, film, and pop songs. The two have different tempos and rhythms. However, they cannot always be used at the same time.
The main difference between a homo-phonic and polyphonic texture is that multiple melodic lines accompany the main melody. The melody is usually in the foreground, while the accompaniment is in the background.
Homophonic textures are commonly found in choral music. However, they can also be found in pop, rock, and dance music. They are often difficult to follow, making a song more enjoyable.
4. Monophonic Texture
A homophonic texture has a single unaccompanied melodic line of music. The term is often a bit confusing, as there are different types of homo-phonic textures.
The earliest forms of monophony were Gregorian chants, which consisted of one melody played by a solo singer. Another type is heterophony, which features contrapuntal harmony. A third type is a polyphony, which is characterized by a series of melodic lines layered to form a unified sound.
During the Middle Ages, composers discovered polyphonic textures. Polyphony consists of multiple voices playing different melodies. They can be simple chords or many complex melodies.
The majority of popular music today has homophonic textures. However, the most sophisticated genres of music are still polyphonic.
The traditional music of the Middle East, Asia, and Europe contain polyphonic textures. During the Middle Ages, classical music favored polyphony. Aside from this, classical music also used heterophony. In the twentieth century, composers such as Igor Stravinsky created imaginative uses of textures.
5. Polyphonic Texture
The homophonic polyphonic texture is a type of music with a rich development of secondary voices. The lower strings with a bass line support the melody.
This type of texture was popular in Renaissance and Baroque periods. During this time, polyphony was the most common musical texture. However, it is not uncommon to hear a piece with a homophonic texture, especially in contemporary pop music.
A polyphonic texture is defined by the Greek word ‘poly,’ which means many. In this case, there is a clear relationship between all the parts, which can be considered independent.
A similar type of texture is the melody-dominated texture. The melody and its accompaniment dominate this type of texture. The most common type of this texture is heard in choral works. The primary part of the melody may be in a higher or lower register, while the accompaniment will often be in a more complicated pattern.
The Instrumental Musical Texture of Homophony
This is another type of homophonic texture which is instrumental. This involves two or more instruments playing the same melody in an alternating pattern. Instruments such as strings and keyboards are commonly used to create this type of texture. Another example is when a single instrument plays multiple notes simultaneously, giving a full and rich sound. This type of music often conveys emotions or feelings, depending on the musical style.