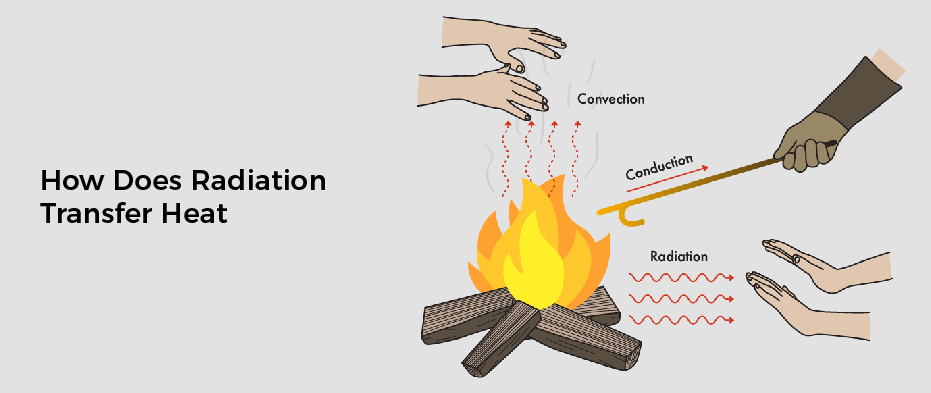
Radiation heat transfer is an important concept to understand when it comes to how heat is transferred from one object to another. This blog post will look at radiation heat transmissionand how it works.
Heat transmissionby radiation is essential to life. A prominent example is the transfer of heat from the surface of the sun to Earth. Because every object above absolute zero emits electromagnetic waves, radiant energy is ubiquitous.
Consequently, managing and mitigating unwanted radiant heat transfer is essential. The reason sunscreens use titanium oxide and zinc oxide is that they reflect sunlight. These chemicals block and scatter the sun’s rays. Solar radiation is also a concern for satellites, which is why the multilayered reflective film is applied to them.
What Is Radiation Heat Transfer?
Radiation heat transfer is the process by which heat is transferred from one object to another via radiation. Radiation heat transmissionis important because it allows us totransmissionHeat from one location to another without having to use any other form of energy. This process is often used in industrial settings, where it’s necessary to quickly transfer large amounts of heat.
Different Types of Radiation
There are five main types of radiation heat transfer: convective, conduction, absorptive, radiative, and thermal radiation. Each type of radiation heat transmissionhas its advantages and disadvantages, and different factors affect each type differently.
- Convective Radiationheat transfer occurs when hot air or vapor moves across a surface, transferring the energy as it does so. This type of radiation heat transmissionis quick and efficient.But can also be dangerous if the temperature difference between the two objects is too large.
- Conduction Radiationheat transmissionhappens when electrons move through a material from one atom or molecule to another atom or molecule. This type of radiation Heat transmissionis slow but reliable – perfect for tasks that don’t require a lot of speed but need consistent results.
- Thermal Radiationoccurs when light waves travel through a medium (like air), heating the surrounding area. This type of radiation Heat Transfer is slow but very gentle – perfect for low-temperature tasks that don’t require a lot of accuracy or precision (like heating liquids).
- Absorption of RadiationWhen radiant or convective radiation hits an object, the object absorbs some of that energy (this happens mostly with radiant radiation). This absorption causes the temperature inside the object to rise (since heat is a form of energy). The amount of absorption depends on how much energy is being radiated by the source – higher-energy waves will absorb more than lower-energy waves will.
- Radiative Heat Transfer: Radiative heating occurs when emissions or absorptions from one object cause a rise or fall in temperature near its surface area. This type of heating is often used when cooling down an object.Because it’s fast and efficient; however, it can also be dangerous if mistakes are made during installation or use.
How Does Radiation Transfer Heat?
Radiation is a type of energy that comes in many different forms. Some examples of radiation are light, heat, sound, and radio waves. Radiation is categorized according to the energy it carries (e.g., electromagnetic radiation, x-rays, gamma rays). Radiation also falls into two main categories:
- Ionizing radiation includes radioactive materials like plutonium and uranium that can break down molecules in your body and cause cancer.
- Non-ionizing radiation includes microwave ovens, cell phones, and sunlight.
Laws govern the use of radiation, and its mechanisms of action are based on the types of particles involved (e.g., photons versus electrons). The three main mechanisms by which radiations transmissionheat are conduction, convection, and radiation exchange (radiation capture).
- Conduction is the slowest heat transfer mechanism because particles move from hotter to colder regions.
- Convection is intermediate between conduction and radiation exchange.Because it allows hot objects to move faster than cold objects but removes thermal energy from the hotter object.
- Radiation exchange is the fastest mode of heat transfer because it eliminates thermal energy from one object and transfers it to another without any contact between them (i.e., infrared).
There are several factors that affect radiant heat transfer: surface area coverage, the temperature difference between sources.And receivers, concentration differences between sources and receivers, emissivity (or reflectivity), surface roughness (i.e., facets), velocity gradients, etc.
Different technologies utilizing radiant heat transfer have been developed in recent years in response to increasing environmental concerns over global warming.As well as safety concerns over potential injuries caused by improper usage or mishandling of thermal sources.
Verdict
Radiation heat transfer is an important concept to understand when it comes to how heat is transferred between objects. There are three main forms of radiation heat transmission: convection, conduction, and thermal radiation. Each type has advantages and disadvantages, and different factors affect each type differently.
Understanding the basics of radiation heat transmission can help you make informed decisions about how you use this technology in your everyday life. It is also important to be aware of the safety considerations associated with radiation heat transfer. Always follow best practices when using this technology!