Climate change can have a major effect on our environment, including the rate of weathering. But what exactly is weathering, and how does climate affect it? Rocks are broken down into soils and sediments by weathering, a process that occurs under the influence of the climate. The weathering or breakdown of rocks in equatorial climates subjected to a lot of rain, humidity, and heat occurs faster than similar rocks in dry and cold climates.In this blog post, we will explore the answers to these questions, looking at how temperature affects it and climate change’s effects on weathering rates. With this information, you can better understand how climate affects our environment and the rate of weathering.
What Is Weathering?
What is weathering? Weathering is the process by which rocks, soil, and other materials are broken down into smaller pieces by physical or chemical forces. This can happen in two ways: abrasion (physical) and dissolution (chemical).
What Causes Weathering?
The main cause of weathering is temperature. Warmer temperatures cause materials to break down faster because they’re easier to work with. In addition, warmer temperatures increase the rate at which water molecules dissolve minerals from rocks and soil. This makes these materials more soluble and easier to break down.
The effects of temperature on the rate of weathering are significant. For example, if you live near a mountain range, your house will be warmer in the summertime because heat travels up mountains better than it does down mountains. This increased temperature will cause your house’s walls to decay faster since they’re exposed to more sunlight and heat than they would be during colder months.
Humidity also has a significant impact on the rate of weathering. Low humidity levels cause materials to dry out quickly, which speeds up their breakdown process due to increased exposure to air particles and sunlight (both of which help break down substances).
In contrast, high humidity levels can prevent materials from drying out completely, which slows their degradation rates due to competition for moisture resources among various plants and microorganisms. Soil science students should note that many physical processes, such as abrasion or mineral dissolution, are significantly affected by moisture availability!
Different Types of Weathering
Here are the different types of weathering and what they involve: Physical Weathering includes abrasion (a rubbing action) and dissolution (a dissolving action).
- Physical weathering includes rock breaking away due to wind or water erosion and earthmoving operations like construction site grading or filling in wetlands. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun also leads to mountain rocks breaking down through photolysis.
- Chemical Weathering – includes oxidation-reduction reactions between metals and water. Oxidation means adding oxygen atoms, while reduction means removing oxygen.
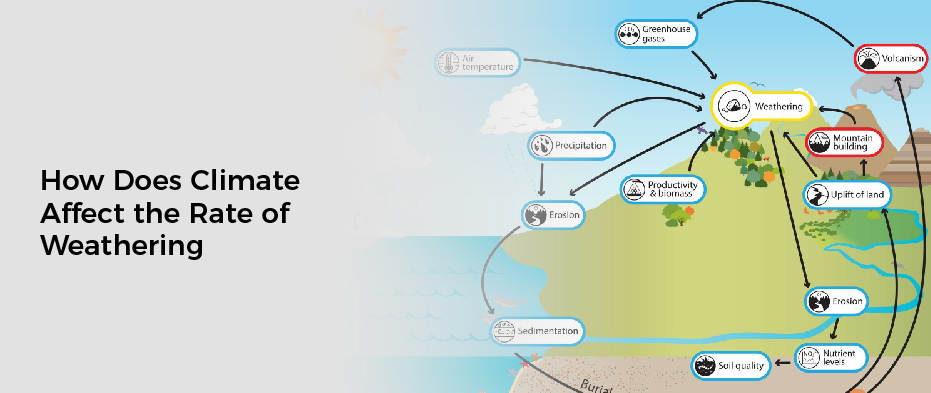
Climate, Temperature & Weathering
There are a few factors that affect the rate of weathering. The effects of temperature and moisture on the rate of weathering are two major factors. When temperatures increase, the rate of water vaporization increases, which speeds up the process of mineralization. Conversely, water vaporization decreases when temperatures decrease, slowing down mineralization rates.
Moisture also impacts how quickly rocks break down into smaller pieces. More moisture means faster rates of rock erosion, while less moisture means slower rates of rock erosion.
Climate conditions also significantly impact how quickly rocks disintegrate under natural conditions. Climate conditions like rainfall and sunshine can influence which types or minerals are most active in breaking down rocks.
Additionally, air pollutants can affect how quickly rocks erode by oxidizing them or altering their composition in some way. This can lead to changes in soil fertility and stability and plant growth patterns – all factors that can influence weathering rates overall.
Understanding how fast rocks are worn down is important for human development and conservation efforts. For example, knowing which types of rocks are being worn away more rapidly than others might help us choose locations for construction or infrastructure that will last longer. Knowing what kindsof climate change are happening now and in the future will also help us plan for future needs like disaster relief or food security.
Investigating The Relationship Between Climate And Weathering Rates
Climate affects the rate of weathering in many ways. The different climates and regions around the world contribute to different weathering rates, which can impact the overall rate of erosion. Temperature, precipitation, and sunlight exposure all play a role in determining how quickly surfaces are worn down.
Higher temperatures cause rocks to expand and contract, leading to more rapid weathering. More precipitation means higher levels of water which can erode surfaces much faster. Sunlight also affects the chemical composition of rocks, which can lead to increased weathering.
Wind contributes to sandblasting, which increases the rate of weathering. Plant roots can create cracks in rocks, leading to faster weathering. Moreover, long-term climate change can lead to drastic changes inweathering rates throughout an area or even globally.
The Effects Of Climate Change On Weathering Rates
Climate is one of the most important factors that affect the rate of weathering. Higher precipitation levels, for example, lead to more erosion and faster wear down of rocks. Temperature also plays a significant role in how quickly rocks break down. When temperatures increase, erosive forces are stronger, and the rate at which rocks can be worn down increases.
Different climates have different weathering rates due to the different soil types found in each area. For example, mountainous regions tend to experience more rapid erosion due to the increased amounts of rainfall that is common there. Additionally, strong winds can create dust storms that help to accelerate the breakdown process by wearing down rocks and boulders.
The effects of global climate change on geology are still being studied in detail, but they will have long-term impacts on everything from geomorphology (the study of landforms) to paleoclimate (the history and dynamics of Earth’s climate).
As we continue emitting greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, temperatures will continue to rise and directly impact how quickly soil breaks down. In particular, elevated carbon dioxide concentrations lead to higher temperatures, which speeds up weathering processes even more!
Conclusion
Understanding how does climate affect the rate of weathering is essential for understanding and protecting our environment. Temperature, humidity, and other climate factors can significantly impact the rate at which natural forces break down rocks. Global climate change will continue to alter weathering rates worldwide, leading to landforms and soil composition changes. By becoming aware of these potential impacts, we can take steps to mitigate their effects and preserve our environment for future generations.
Take action today! Learn more about climate change and its effects on weathering so that you can help protect your local environment for years to come.