Are you an animal lover with a longing to lend a helping hand to our furry friends? If so, you may be considering a career as a veterinarian. But before you dive into the world of stethoscopes and scalpels, there are a few education requirements you need to be aware of.
From high school education to specialized training options, the path to becoming a veterinarian is filled with rigorous academic challenges and hands-on experiences. So, let’s explore the exciting journey that awaits you in the realm of veterinary medicine.
High School Education
In order to pursue a career as a veterinarian, you must first complete a high school education. Obtaining a high school diploma is the starting point for your journey towards becoming a veterinarian. During your high school years, it’s important to focus on science and math courses, as they’ll provide a solid foundation for your future studies in veterinary medicine.
Science classes such as biology, chemistry, and physics will give you a fundamental understanding of the scientific principles that are essential in veterinary medicine. These courses will introduce you to the basics of anatomy, physiology, and genetics, which are all critical areas of study for veterinarians. Math courses like algebra and statistics will help you develop problem-solving and analytical skills, which are valuable in diagnosing and treating animals.
Additionally, taking advanced placement (AP) or honors courses in these subjects can demonstrate your dedication and academic ability to veterinary schools during the application process. It’s also beneficial to participate in extracurricular activities related to animals, such as volunteering at animal shelters or working at a veterinary clinic.
A high school education is the first stepping stone towards becoming a veterinarian. By focusing on science and math courses, as well as gaining practical experience through extracurricular activities, you’ll be setting yourself up for success in your future veterinary studies.
Undergraduate Degree
Now that you’ve completed high school, it’s important to understand the requirements for obtaining an undergraduate degree in order to become a veterinarian.
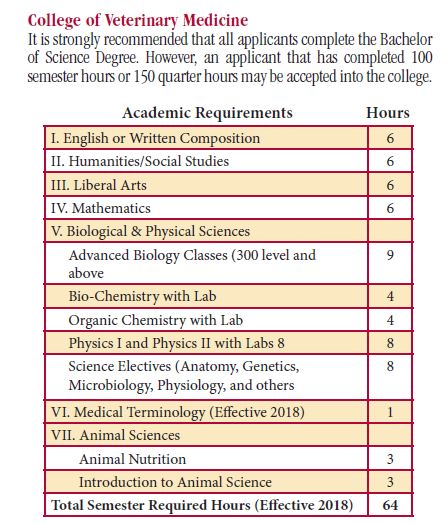
A bachelor’s degree is necessary for admission to veterinary school, and most programs require completion of specific pre-veterinary courses. These courses typically cover subjects such as biology, chemistry, physics, and math, providing a strong foundation for the advanced coursework you’ll encounter in veterinary school.
Bachelor’s Degree Requirements
You can earn a Bachelor’s degree in order to meet the requirements for becoming a veterinarian. A Bachelor’s degree is typically the first step in your journey towards a career in veterinary medicine. To pursue this degree, you’ll need to complete a four-year undergraduate program at a recognized college or university.
While there’s no specific major required for admission into veterinary school, it’s recommended that you focus on courses in the sciences, such as biology, chemistry, and anatomy. These courses will provide you with a strong foundation in the biological sciences, which is essential for understanding the health and anatomy of animals.
Additionally, you may also be required to complete courses in mathematics, English, and social sciences as part of your Bachelor’s degree program.
Pre-Veterinary Course Prerequisites
To meet the prerequisites for a pre-veterinary course, completing an undergraduate degree is necessary. It’s important to note that the specific requirements may vary between different veterinary schools.
However, there are some common prerequisites that most schools require. These typically include courses in biology, chemistry, physics, mathematics, and English. The purpose of these prerequisites is to provide students with a strong foundation in the sciences and critical thinking skills needed for success in veterinary school.
Additionally, some schools may require courses in animal science, microbiology, genetics, or other related subjects. It’s crucial to research the specific prerequisites of the veterinary schools you’re interested in to ensure you meet all the requirements before applying.
Pre-Veterinary Courses
To prepare for a career in veterinary medicine, you’ll need to complete a series of pre-veterinary courses. These courses typically include core science subjects such as biology, chemistry, and physics, which provide a foundation for understanding animal health and physiology.
Additionally, you may be required to take specific animal health prerequisites, such as animal nutrition and anatomy, to gain a deeper understanding of the field.
Core Science Courses
Core science courses, including biology, chemistry, and physics, are essential prerequisites for aspiring veterinarians. These courses provide the foundation for understanding the biological processes and chemical reactions that occur within animals.
Biology introduces students to the study of living organisms, allowing them to gain knowledge about animal anatomy, physiology, and genetics.
Chemistry focuses on the composition, properties, and transformations of matter, which is crucial for understanding the chemical reactions that occur in the body.
Physics, on the other hand, helps veterinarians understand the principles behind energy, motion, and force, which are fundamental concepts in veterinary medicine.
Animal Health Prerequisites
Before pursuing a career as a veterinarian, it’s important to complete animal health prerequisites, also known as pre-veterinary courses. These courses are designed to provide you with a strong foundation in the biological and physical sciences that are essential for understanding animal health and disease.
Animal health prerequisites typically include courses in biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics. In biology courses, you’ll learn about the structure, function, and behavior of animals, as well as the basics of genetics and evolution.
Chemistry courses will cover the principles of organic and inorganic chemistry, while physics courses will teach you about the principles of motion, energy, and heat. Mathematics courses will help you develop the quantitative skills necessary for analyzing data and making calculations in veterinary medicine.
Veterinary College Admission Test (VCAT)
Taking the Veterinary College Admission Test (VCAT) is an essential step towards pursuing a career as a veterinarian. This standardized test evaluates your knowledge and skills in various areas related to veterinary medicine. It’s designed to assess your readiness for veterinary school and determine if you have the necessary academic foundation to succeed in the field.
The VCAT consists of multiple-choice questions that cover a wide range of subjects, including biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics. You’ll need to demonstrate your understanding of these fundamental sciences, as well as your ability to apply that knowledge to real-world scenarios. Additionally, the test may also include questions related to animal anatomy, physiology, and clinical medicine.
Preparing for the VCAT requires a solid understanding of the core concepts in these areas. It’s recommended to review your undergraduate coursework and supplement your knowledge with additional study materials, such as review books and practice exams. Familiarizing yourself with the format and content of the test will help you feel more confident and perform your best on exam day.
Scoring well on the VCAT is crucial for gaining admission to veterinary school. Each school has its own requirements and standards for admission, but a strong performance on the VCAT can significantly enhance your application. Therefore, it’s important to invest time and effort into preparing for this test to increase your chances of being accepted into a veterinary program.
Veterinary College Application Process
To successfully apply to veterinary college, you’ll need to complete a series of steps in the application process.
The first step is to research and identify the veterinary colleges that best align with your career goals and interests. Once you have selected the colleges you’re interested in, you’ll need to gather all the necessary application materials, including transcripts, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement.
Next, you’ll need to complete the Veterinary College Admission Test (VCAT) if it’s required by the colleges you’re applying to. The VCAT is a standardized test that assesses your knowledge and skills in various areas related to veterinary medicine.
After completing the necessary tests and gathering all the required materials, you can begin the application process. This typically involves filling out an online application form and submitting all the required documents to each veterinary college. It’s important to pay attention to deadlines and ensure that all materials are submitted on time.
Once your application has been submitted, you may be invited for an interview. The interview is an opportunity for the admissions committee to get to know you better and assess your suitability for their program.
Veterinary College Curriculum
When it comes to the veterinary college curriculum, you can expect to take a variety of core veterinary courses that will provide you with a strong foundation in the field. These courses will cover essential topics such as animal anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and pathology.
Additionally, many veterinary colleges offer specialized elective options that allow you to tailor your education to your specific interests and career goals.
Core Veterinary Courses
In the Veterinary College Curriculum, you’ll cover a variety of core veterinary courses. These courses are designed to provide you with the foundational knowledge and skills necessary to become a successful veterinarian.
Some of the core courses you can expect to take include:
- Anatomy and physiology: This course will give you a comprehensive understanding of how the animal body functions.
- Pharmacology: This course will teach you about how drugs and medications interact with the body.
- Pathology: In this course, you’ll learn about how diseases develop and progress.
- Microbiology: This course will cover how microorganisms affect animal health.
- Animal behavior: This course will explore how animals behave and communicate.
These courses will give you a comprehensive understanding of how the animal body functions, how drugs and medications interact with the body, how diseases develop and progress, how microorganisms affect animal health, and how animals behave and communicate.
Additionally, you’ll also take courses in veterinary medicine and surgery. In these courses, you’ll learn about diagnosing and treating various illnesses and injuries that animals may experience.
Specialized Elective Options
You have a range of specialized elective options to choose from in the Veterinary College Curriculum. These electives allow you to explore specific areas of veterinary medicine that align with your interests and career goals.
One option is to take courses in exotic animal medicine, where you can learn about the unique challenges and care requirements of non-traditional pets like reptiles, birds, and small mammals.
Another option is to delve into wildlife medicine, which focuses on the health and conservation of wild animals.
If you’re interested in research, you can choose electives in veterinary pathology or epidemiology to gain a deeper understanding of disease processes and their impact on animal populations.
Additionally, there are elective options in equine medicine, small animal surgery, and even alternative therapies like acupuncture and herbal medicine.
With these specialized electives, you can tailor your education to suit your specific interests and pave the way for a fulfilling career as a veterinarian.
Clinical Rotations and Internships
To gain practical experience, aspiring veterinarians must complete clinical rotations and internships. These hands-on opportunities allow you to apply the knowledge and skills you’ve acquired in the classroom to real-life situations. Clinical rotations typically take place during the final years of your veterinary education and provide you with the chance to work directly with experienced veterinarians in various specialties. This allows you to gain exposure to a wide range of medical cases and develop the essential clinical skills needed in veterinary practice.
Internships, on the other hand, are more in-depth and comprehensive. They usually last for one year and provide you with intensive training in a specific area of veterinary medicine. During your internship, you’ll work closely with board-certified specialists and experienced veterinarians, honing your skills and expanding your knowledge in your chosen field. This hands-on experience not only helps you become a more competent and confident veterinarian but also provides you with valuable networking opportunities and connections within the veterinary community.
Clinical rotations and internships are crucial steps in your journey to becoming a veterinarian. They offer you the chance to gain practical experience, develop your clinical skills, and build a solid foundation for your future career. Make the most of these opportunities, actively engage with your mentors, and seize every learning opportunity that comes your way.
Licensing and Certification
Obtaining a veterinary license is a necessary step for practicing veterinarians. Once you have completed your veterinary degree, you’ll need to pass the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE) in order to become licensed.
The NAVLE is a comprehensive exam that assesses your knowledge and competence in various areas of veterinary medicine. It’s administered by the International Council for Veterinary Assessment (ICVA) and is recognized by all licensing boards in the United States and Canada.
In addition to the NAVLE, you may also need to fulfill other licensing requirements specific to your state or province. These requirements may include completing a certain number of hours of supervised clinical experience, submitting an application with the appropriate fees, and passing a state or provincial jurisprudence exam.
It’s important to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the licensing board in the jurisdiction where you plan to practice.
Once you have obtained your veterinary license, it’s important to maintain it by fulfilling any continuing education requirements mandated by your licensing board. These requirements may include attending seminars, workshops, or conferences, or completing online courses. By staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in veterinary medicine, you can ensure that you’re offering the best possible care to your animal patients.
Continuing Education Requirements
After obtaining your veterinary license, it’s crucial to stay updated in the field by fulfilling the continuing education requirements mandated by your licensing board. Continuing education is essential to keep your knowledge and skills current, ensuring that you’re providing the best possible care to your patients. These requirements vary by state and licensing board, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with the specific guidelines applicable to you.
Continuing education can take many forms, including attending conferences, workshops, and seminars, as well as completing online courses or participating in webinars. The goal is to engage in activities that enhance your understanding of new medical advancements, treatment techniques, and best practices in veterinary medicine. By staying informed, you can provide cutting-edge care and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving field.
Most licensing boards require a certain number of continuing education hours over a specified period, such as every two or three years. It’s essential to carefully track and document your participation in these educational activities to ensure compliance. Failure to meet these requirements can result in penalties, including license suspension or revocation.
Continuing education not only benefits your professional development but also demonstrates your commitment to providing high-quality care. By staying current, you can offer the best possible treatment options to your animal patients and maintain your professional standing as a veterinarian.
Specialization and Advanced Training Options
Consider pursuing specialization and advanced training options to further enhance your veterinary skills and expand your career opportunities. As a veterinarian, you have the opportunity to focus on a specific area of veterinary medicine that aligns with your interests and passion. Specializing in a particular field allows you to develop expertise and provide specialized care to animals in need.
One option for specialization is to become a board-certified veterinary specialist. This requires completing a residency program in your chosen specialty, which typically lasts for three to four years. During this time, you’ll receive intensive training and mentorship from experienced specialists in your field. After completing your residency, you’ll need to pass a rigorous examination to become board-certified.
Another option for advanced training is to pursue a Master’s or Ph.D. degree in veterinary science or a related field. This can open up opportunities for research and teaching positions within academia or industry. Advanced degrees can also give you a competitive edge when applying for leadership roles or positions in veterinary organizations.
In addition to specialized training, continuing education courses and conferences can help you stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in veterinary medicine. These opportunities allow you to expand your knowledge and skills in specific areas of interest.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Typically Take to Complete the Undergraduate Degree Required for Veterinary School?
Typically, it takes about four years to complete the undergraduate degree required for veterinary school. During this time, you will gain the necessary knowledge and skills to prepare you for the next step in your veterinary career.
Are There Any Specific High School Courses or Extracurricular Activities That Can Help Prepare Students for a Career in Veterinary Medicine?
Taking specific high school courses in biology, chemistry, and math can help prepare you for a career in veterinary medicine. Additionally, participating in extracurricular activities related to animals or science can provide valuable experience and make your application more competitive.
What Is the Average GPA and GRE Scores Required for Admission Into Veterinary School?
To get into veterinary school, you’ll need a good GPA and GRE scores. The average requirements vary among schools, so it’s best to check their specific admissions criteria to see what they’re looking for.
Can I Apply to Multiple Veterinary Schools at the Same Time?
Yes, you can apply to multiple veterinary schools at the same time. It’s a good idea to have backup options and increase your chances of acceptance. Just make sure to carefully manage your application deadlines and requirements.
Are There Any Specific Requirements or Exams That Need to Be Completed for Licensing and Certification as a Veterinarian?
To become a licensed veterinarian, you need to fulfill specific requirements and pass exams. These exams and requirements vary by state and country, so it’s important to research and understand the regulations in your area.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully navigated the education requirements for becoming a veterinarian. By completing high school, obtaining an undergraduate degree, and taking pre-veterinary courses, you have set yourself on the path to a fulfilling career.
After passing the Veterinary College Admission Test and completing veterinary college, you can gain valuable experience through clinical rotations and internships.
Remember to stay up to date with licensing and certification requirements and consider pursuing specialization or advanced training options.
Keep up the great work!