Where does the Calvin cycle occur: Many of us have heard of it, but do we really understand what it is and where it takes place? The Calvin cycle is essential to photosynthesis, taking in carbon dioxide to create energy for plants and other organisms. Although this process occurs within all green plants, from algae to grasses, many people are unsure exactly how and where it happens. In this blog post, explore the intricacies of the Calvin Cycle.And discover why it’s such an important element for life on Earth!
What Is Calvin Cycle?
The Calvin cycle is a set of biochemical reactions that take place during photosynthesis. The process plants use to convert light energy into chemical energy. It is named after Melvin Calvin, who received the 1961 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on discovering these reactions.
Why is the CalvinCycle Is Important Element for Human Life?
The Calvin cycle is an important element of human life, as it helps maintain a healthy and balanced atmosphere. Removing carbon dioxide from the environment and releasing oxygen helps regulate the Earth’s climate, allowing us to live and thrive on this planet.
In addition, the cycle’s energy-rich molecules can feed plants and animals, making it a vital part of the global food system. Lastly, photosynthesis also helps us produce renewable energy sources, such as biomass and biofuels, which can power our homes and vehicles. Without this cycle, many aspects of human life would not exist.
Where Does the Calvin Cycle Occur?
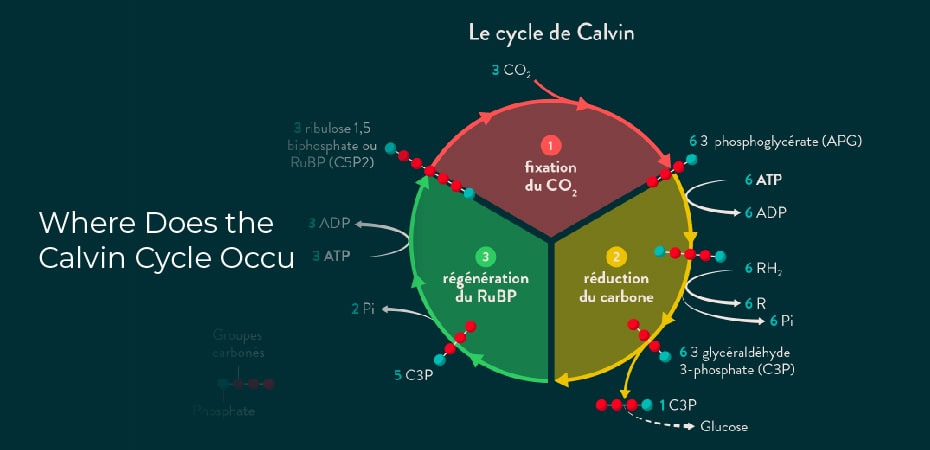
The Calvin cycle occurs within chloroplasts, which are small organelles found in plants and other photosynthetic organisms such as algae. Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis, where the energy from light is absorbed by pigments such as chlorophyll.And then used to drive chemical reactions that produce energy-rich sugars. The Calvin cycle takes place within these organelles, using the energy from light to convert carbon dioxide into sugars.
What Is the Function of the Calvin Cycle?
The primary function of the Calvin cycle is to produce glucose and other energy-rich molecules for use by plants. The reaction produces many other compounds, such as oxygen and other small molecules, released as byproducts. In addition to providing energy for the plant, the Calvin cycle also helps regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, removing some of this molecule from its environment. This process is important for maintaining Earth’s climate.
What Are the Steps in the Calvin Cycle?
The Calvin cycle is a complex series of reactions.But the most important steps are as follows: Carbon dioxide enters the chloroplast.And combines with the enzyme rubisco to produce 3-phosphoglycerate. This molecule is then converted to glycerate-3-phosphate, which is further processed into glucose and other molecules. The plant can use the glucose for energy or store it in cells for later use. The cycle also produces oxygen as a byproduct, which is released into the environment.
The Benefit ofCalvinCyclefor Plants
The Calvin cycle provides numerous benefits for plants. It allows them to use light energy from the sun to produce their own food in the form of glucose, an important source of energy for plant growth and development. The process also helps regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, as it takes some of this gas out of its environment and uses it as an energy source. This reduces the number of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, making it easier for plants to flourish. Finally, oxygen is produced as a byproduct of the cycle, which helps support all forms of life on Earth.