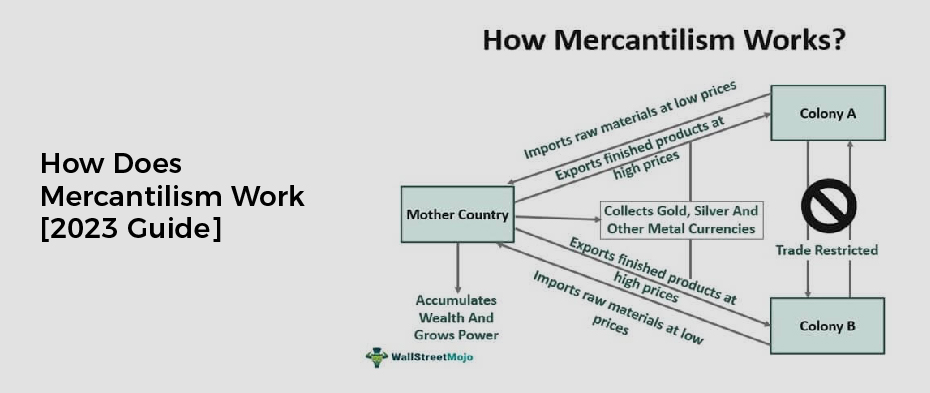
Mercantilism is a form of economic policy that has been used by many nations throughout history and is still used in some countries today. It has both advantages and disadvantages. If you have ever wondered how mercantilism works, then this blog post is for you. By the end of this post, you will better understand how does mercantilism work.
What Is Mercantilism?
Mercantilism is a theory and practice of economic regulation and expansion developed in the 17th and 18th centuries. It is based on the belief that a country’s wealth depends on its gold and silver reserves and its trade surpluses with other nations.
Mercantilism was designed to increase a country’s economic power and heavily relied on exports over imports. This was done in order to establish colonies for an empire, support domestic manufacturers with tariffs, influence currency to gain an advantage in overseas trade, and hold onto gold and silver as valuable assets.
Despite having some positive effects on global trade, mercantilism also had some negative impacts. For example, mercantilism led to increased nationalism and protectionism, which restricted international trade. Additionally, it caused inflation due to the overvalued value of gold and silver.
Origins And Characteristics Of Mercantilism
Mercantilism is an economic theory that originated in the 16th century and continues to be practiced in various ways around the world today. It’s typically defined as maximizing national wealth through increased exports and reduced imports.
Mercantilism has a long history, dating back to when nations first began to trade with each other. At its core, mercantilism is rooted in the belief that countries are competing against one another for resources. So countries need to engage in as much trade as possible in order to maintain or increase their wealth.
While mercantilism has many strengths and weaknesses, at its core, it serves an important purpose. Mercantilism helps increase GDP by increasing exports and reducing imports, leading to more jobs and higher wages.
Additionally, it can help countries build up their military forces by acquiring new weapons and technology. However, potential conflicts could arise from this type of policymaking, such as when one country tries to restrict or monopolize imports from another country.
Mercantilism is still practiced in various ways around the world today. For example, some nations have adopted free trade policies while others have implemented protectionist measures. In addition, some countries have turned towards outright mercantilism by engaging in currency manipulation.Or other forms of economic aggression (i.e., forcing other countries to Partner with them economically). While mercantilism may not be the ideal policy option for all nations at all times, it remains an important part of global economics and politics.
Principles Of Mercantilism And Their Effect On Economics
Mercantilism is a theory that was developed in the 16th and 17th centuries to help explain and regulate international trade. Mercantilism is based on the principle that trade between nations should be focused on acquiring as much gold, silver, and other precious metals as possible. This would help increase the country’s economic power.And wealth, allowing them to expand its territory and influence further into the world.
Today, mercantilism is still a relevant theory in economics. It plays an important role in understanding how international trade works and determining which countries are able to prosper economically. Mercantilism also significantly impacts modern economic policymaking by influencing ideas about free trade and protectionism.
Examples Of Mercantilism Today
Mercantilism has a long history dating back to ancient times. For example, during China’s Warring States period (475-221 BC), rulers attempted to increase state revenue by imposing discriminatory taxes on imported goods. Similarly, during Japan’s Heian period (794-1185), rulers tried to increase state revenue by banning or taxing imported items such as silk and tea.
Today, mercantilism still plays an important role in global economies. For example, China is currently the world’s largest trader and producer of goods.As a result, Beijing has strong incentives to restrict imports in order for Chinese businesses to remain competitive globally. Similarly, many countries with strong economic ties with Europe – such as India.They have adopted some form of mercantilist policy in order to strengthen their ties with Europe and protect their industries from foreign competition.
But while mercantilism may be successful in boosting national economic output at first glance, there are several disadvantages associated with this type of economy. The restriction or ban of importation may cause shortages or famines when domestic production is insufficient to meet demand.As happened during the Spanish Economic Crisis in 1876-1879 (when restrictive trade policies caused severe poverty and drought).
Furthermore, since exports are taxed more than imports (to create a balance between trade deficits/surpluses), wealthier countries benefit economically.And gain political power over poorer countries that cannot afford these higher taxes. As a result, many developing nations feel exploited by wealthier nations that use their power as trading partners for strategic purposes.
Final Thoughts About How Does Mercantilism Work
Mercantilism is a form of economic policy that has been used by many nations throughout history and is still in use today. It was designed to increase a country’s economic power, heavily relying on exports over imports.And maximize national wealth through increased exports and reduced imports.
Although mercantilism has positively affected global trade. It also comes with disadvantages, such as increased nationalism and protectionism, inflation due to the overvaluation of gold and silver, and exploitation of poorer countries.