Understanding what type of sugar our DNA has is vitally important for understanding how it functions. Knowing the composition and structure of different types of sugars can give us a better insight into how our genetic material works – which unlocks potential when addressing anything from chronic diseases to evolutionary biology.
This post will explore what type of sugar makes up DNA, why this is so significant, and how that knowledge is being used today. So, keep reading to find out more about one of the most crucial aspects of biochemistry!
The Difference Between DNA & RNA
DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids found in living things, but they have some important differences. DNA is a double-stranded molecule made up of four nucleotides forming the genetic code for all life forms. This code is passed from parent to offspring through sexual reproduction.
Conversely, RNA is a single-stranded molecule composed of four nucleotides that are used to translate the genetic code of DNA into proteins. These proteins are essential for many cellular processes, such as forming important enzymes for energy production or passing genetic information from parent to child during reproduction.
What Is DNA & What Does It Do in The Body?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and is a molecule that contains the instructions an organism needs to develop, live, and reproduce. In humans, most DNA is in the form of chromosomes within the cell’s nucleus.
DNA provides instructions for making proteins, which are essential for body functions such as growth and metabolism. A gene’s sequence of DNA molecules is used as a code to make protein molecules. When these proteins are produced, they carry out the instructions encoded in the DNA. For example, some proteins help form cell structures and regulate metabolism, while others are involved in forming important enzymes used for energy production or passing genetic information from parent to child during reproduction.
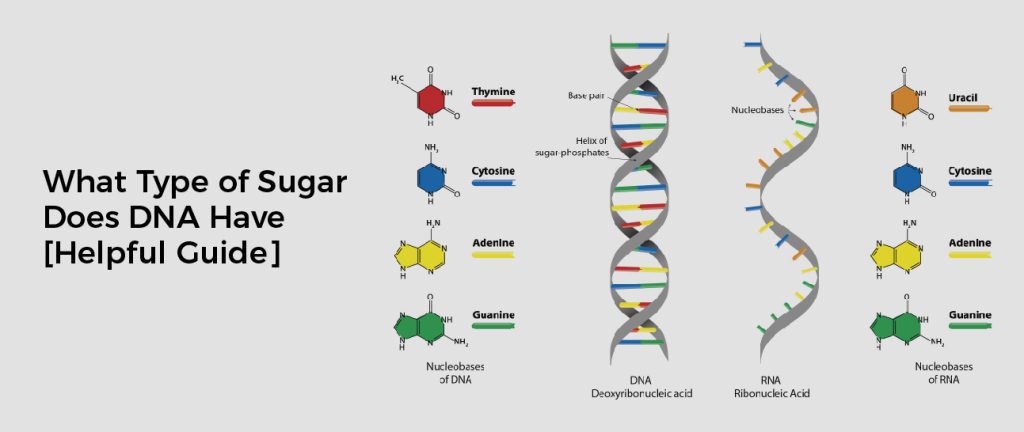
What Type of Sugar Does DNA Have?
DNA is composed of two strands that are intertwined to form a double helix. It consists of four types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Each strand contains millions of these nucleotides, which pair together in specific patterns, forming the instructions for all cellular processes.
The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, a pentose sugar that forms the backbone of the DNA double helix. This sugar makes up the “rungs” of the ladder-like structure formed by the double helix and provides stability to keep it held together.
In humans, DNA provides instructions to build and maintain our bodies. It helps guide the growth, development, and functioning of all the cells that make up our body. The genetic information stored in DNA is passed down from generation to generation, giving us the characteristics that make us unique. This genetic code also guides how we look, how certain organs work, and even influences our behavior.
The Benefits of Understanding the Replication Process
As you know well, understanding the replication process is important for a variety of reasons. For example, it helps us better understand how genes are passed down from generation to generation and how genetic diseases are inherited. It also has implications for medical diagnosis, as mutations in DNA can lead to illnesses such as cancer or other hereditary disorders. By understanding DNA replication, scientists can develop more effective treatments and therapies for these conditions.
How Sugar Is Involved in The Replication Of DNA
The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, a pentose sugar that forms the backbone of the DNA double helix. This sugar provides stability to keep the two strands of DNA together.And helps form hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide bases (A-T and G-C). During replication, both double helix strands unwind and separate so new strands can be created. This process requires the addition of complementary nucleotides, molecules forming pairs with those already on the DNA strand.
The sugar in DNA helps to provide an energy source needed for this process.And is essential for accurately copying the genetic code. Without it, errors may occur during replication, which could lead to genetic defects.
What Recent Research Has Revealed About Sugar & DNA Replication
Recent studies have revealed that sugar plays a much more complex role in DNA replication than previously thought. For example, researchers have found that certain sugars can impact the rate at which strands of the double helix are unwound, as well as how quickly new nucleotides are added to existing strands. They have also identified specific enzymes involved in the replication process.That are sensitive to changes in the concentration of different sugars.